血管新生阻害活性を有するサメ抽出脂質のメカニズムと臨床への応用
2006年3月9日、GTCbioによってアメリカ・サンディエゴで開催されたAngiogenesis research & Theraputicsのポスターセッションにて、強い血管新生阻害活性を有するサメ抽出脂質のメカニズムと臨床への応用についての発表がありました。
An Ethanolic extract from a shark having potent anti-angiogenic activity: its anti-angiogenic mechanism and clinical application
Abstract
An ethanol extract from shark muscle has been shown to have potent angiogenic activity when mixed together with olive oil in a ratio of 1part extract to 9 parts olive oil. This mixture has been given the trade name SuperMaco (SMO).
The anti-angiogenic activity was evident in both in vitro and in vivo studies in rats. When combined with the known angiogenic stimulatory growth factors Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF), Platelet Derived Growth Factor (PDGF), Transforming Growth Factor-Beta ( TGF-β) and Fibroblast Growth Factor -2 (FGF-2), SMO completely eliminated the stimulation induced by these growth factors. Possible mechanisms for this activity are that SMO is competing for receptor sites on the endothelial cell surface by preferential binding to those sites or by binding to the growth factors themselves. Studies were conducted using soluble forms of VEGF-R1 and VEGF-R2 and it was found that SMO inhibited complex formation of the VEGF with both receptors. This inhibitory effect by SMO was enhanced when SMO was pre-incubated with VEGF receptors.
In another study, the effect of SMO on VEGF receptor phosphorylation using human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC) and a human breast carcinoma cell line (MDA-MB-231) was investigated. The in vitro cell proliferation assay indicated that SMO reversed the increase in VEGF promoted cell proliferation in both HUVEC and MDA-MB-231 cells. Using Western Blot analysis it was observed that SMO significantly inhibited VEGF promoted VEGF receptor-1 , VEGF receptor-2 and tyrosine phosphorylation in HUVEC and MDA-MB-231 cells in a dose related manner. These results suggest that SMO appears to block the binding of VEGF with the receptors and inhibit the signal transduction pathways.
-
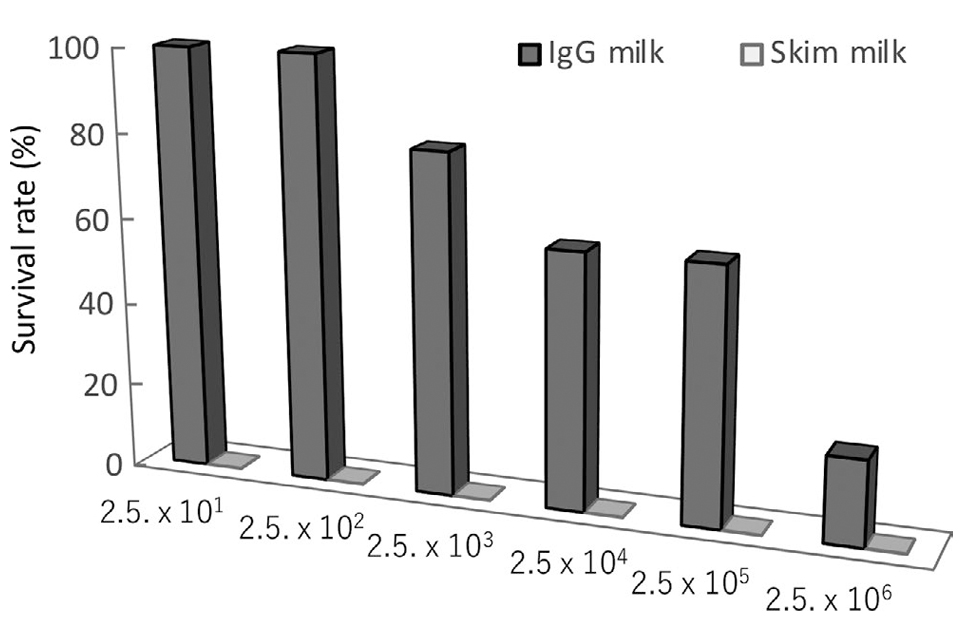 生乳由来IgG高含有濃縮乳清タンパクによるO157、サルモネラ菌、非定型抗酸菌の感染に対する防御力Enriched bovine IgG fraction prevents infections with Enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7, Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis, and Mycobacterium avium
生乳由来IgG高含有濃縮乳清タンパクによるO157、サルモネラ菌、非定型抗酸菌の感染に対する防御力Enriched bovine IgG fraction prevents infections with Enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7, Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis, and Mycobacterium avium
-
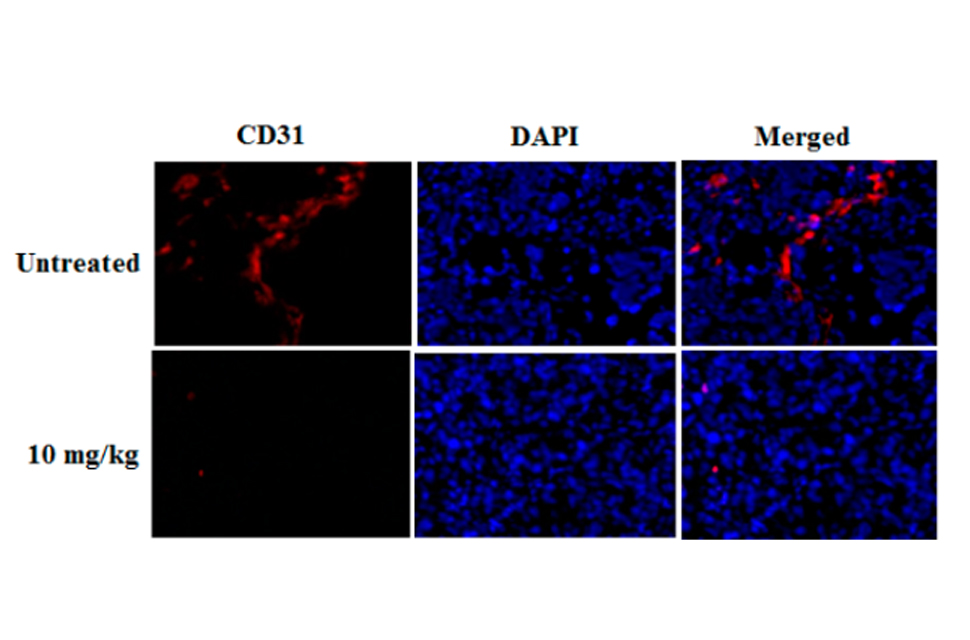 ノコギリヤシ色素の肝細胞がんへの補助療法の可能性New Natural Pigment Fraction Isolated from Saw Palmetto: Potential for Adjuvant Therapy of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
ノコギリヤシ色素の肝細胞がんへの補助療法の可能性New Natural Pigment Fraction Isolated from Saw Palmetto: Potential for Adjuvant Therapy of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
-
 ノコギリヤシ色素の血管新生抑制効果Red pigment from Saw palmetto: A natural product for potential alternative cancer treatment
ノコギリヤシ色素の血管新生抑制効果Red pigment from Saw palmetto: A natural product for potential alternative cancer treatment
-
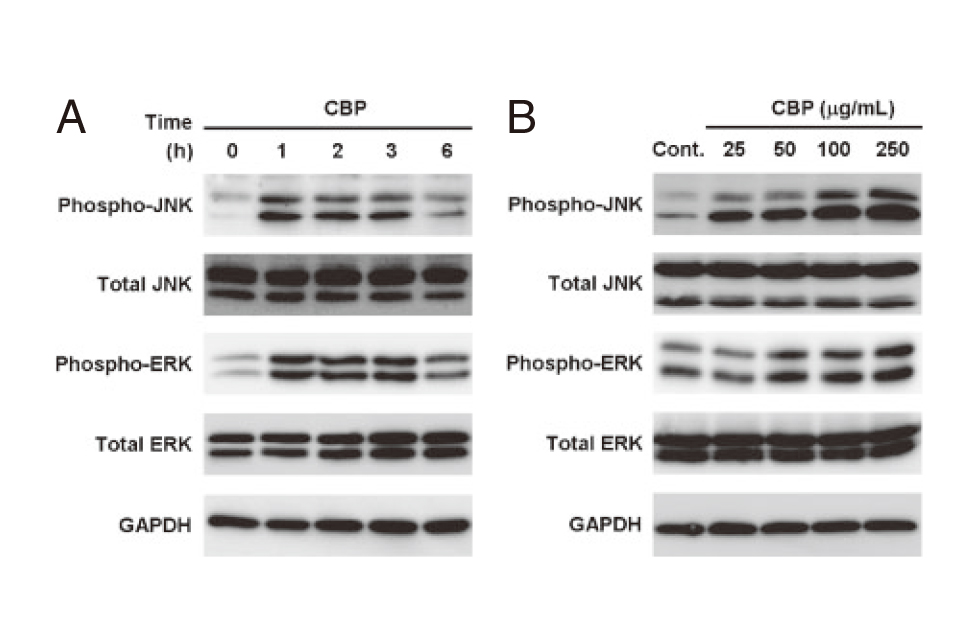 CBPのJNK-ATF4経路活性化による骨形成促進CBP Facilitate Osteogenesis through Activation of the JNK-ATF4 Pathway
CBPのJNK-ATF4経路活性化による骨形成促進CBP Facilitate Osteogenesis through Activation of the JNK-ATF4 Pathway
-
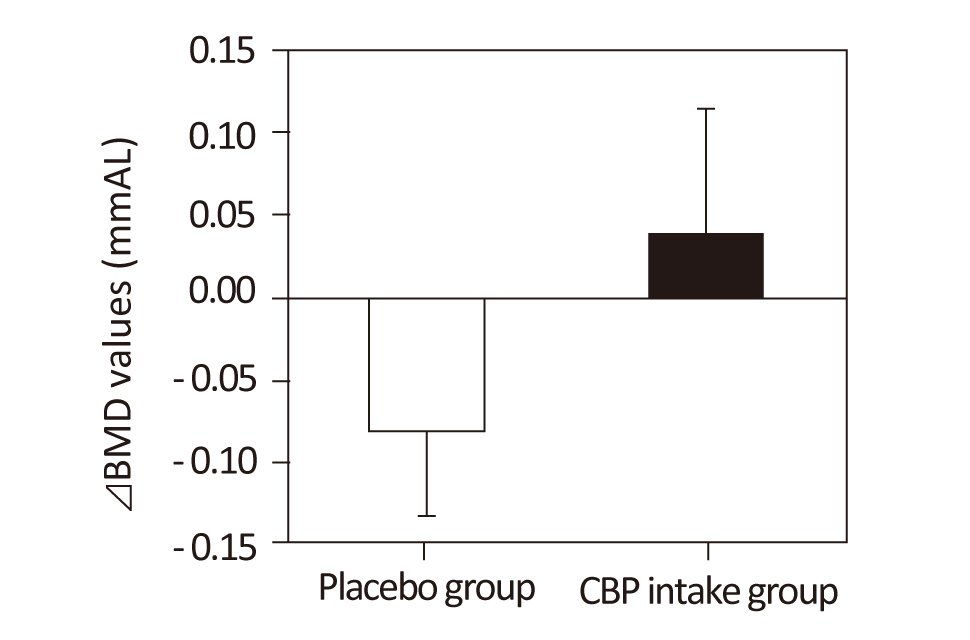 乳清活性タンパク質 (Concentrated-Bovine Protein; CBP) の骨密度に対する上昇効果の検証
乳清活性タンパク質 (Concentrated-Bovine Protein; CBP) の骨密度に対する上昇効果の検証
-
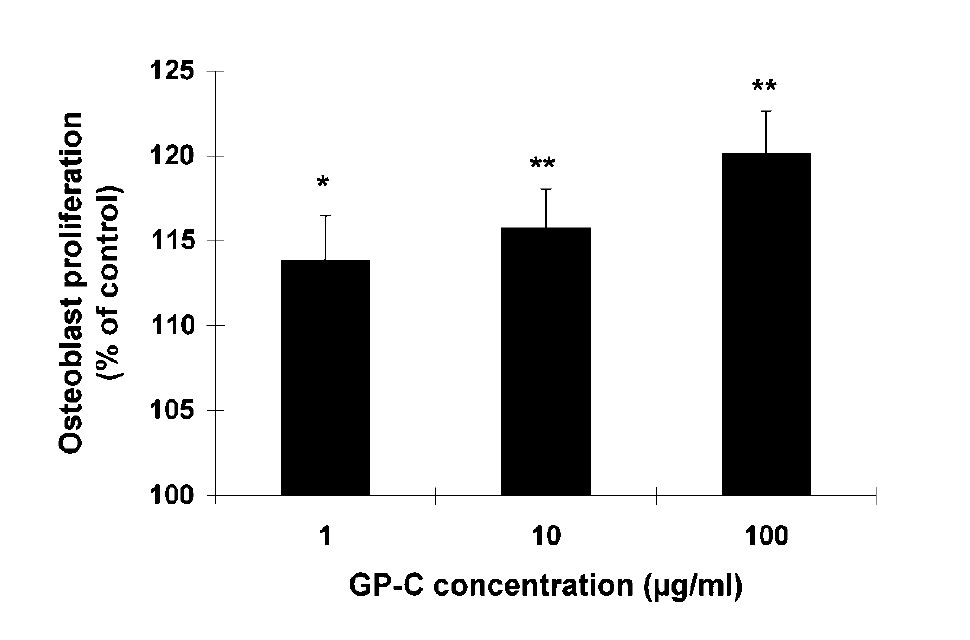 初乳による人間の骨の成長と発達を促進する可能性Effect of a Growth Protein-Colostrum Fraction on Bone Development in Juvenile Rats
初乳による人間の骨の成長と発達を促進する可能性Effect of a Growth Protein-Colostrum Fraction on Bone Development in Juvenile Rats
-
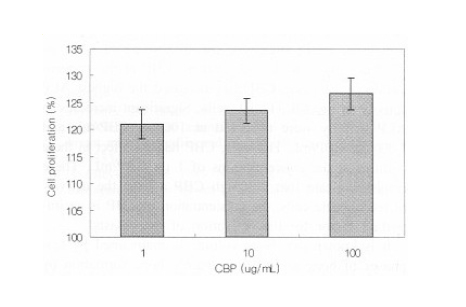 濃縮乳清タンパク質(CBP)の効果:骨芽細胞増殖と骨代謝の促進作用Effects of Colostrum Basic Protein from Colostrum Whey Protein: Increased in Osteoblast Proliferation and Bone Metabolism
濃縮乳清タンパク質(CBP)の効果:骨芽細胞増殖と骨代謝の促進作用Effects of Colostrum Basic Protein from Colostrum Whey Protein: Increased in Osteoblast Proliferation and Bone Metabolism
-
 血管新生阻害活性を有するサメ抽出脂質のメカニズムと臨床への応用An Ethanolic extract from a shark having potent anti-angiogenic activity: its anti-angiogenic mechanism and clinical application
血管新生阻害活性を有するサメ抽出脂質のメカニズムと臨床への応用An Ethanolic extract from a shark having potent anti-angiogenic activity: its anti-angiogenic mechanism and clinical application
-
 サメ抽出脂質によるがん増殖や転移の抑制Shark Lipids for Treatment of Malignant Diseases
サメ抽出脂質によるがん増殖や転移の抑制Shark Lipids for Treatment of Malignant Diseases
-
 サメ抽出脂質による悪性疾患治療Inhibition of Cancer Growth and Metastases by Preparations Based on Shark Oil
サメ抽出脂質による悪性疾患治療Inhibition of Cancer Growth and Metastases by Preparations Based on Shark Oil
-
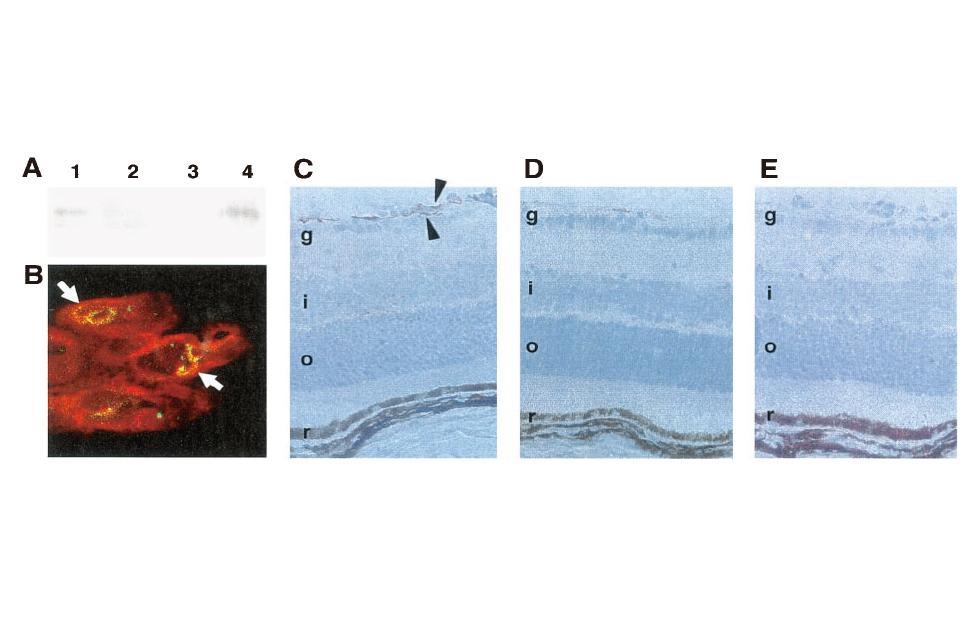 レプチンは虚血誘発性網膜血管新生を刺激するLeptin Stimulates Ischemia-Induced Retinal Neovascularization
レプチンは虚血誘発性網膜血管新生を刺激するLeptin Stimulates Ischemia-Induced Retinal Neovascularization
-
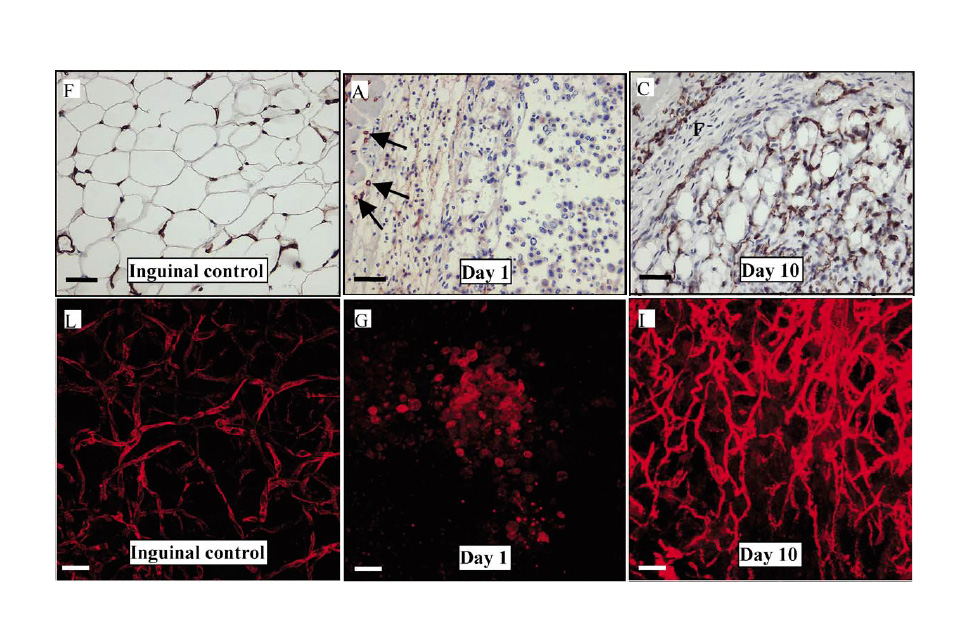 脂肪組織と血管新生の関係Angiogenesis in an in vivo model of adipose tissue development
脂肪組織と血管新生の関係Angiogenesis in an in vivo model of adipose tissue development
-
 サメ抽出脂質の抗腫瘍効果機能性食品(アガリクスタケ、タモギタケ、ヤマブシタケ、アラビノキシラン、サメ軟骨、およびサメ抽出脂質)の摂取がマウスL M 8 Dunn 骨肉種移植腫瘍の成長に及ぼす効果
サメ抽出脂質の抗腫瘍効果機能性食品(アガリクスタケ、タモギタケ、ヤマブシタケ、アラビノキシラン、サメ軟骨、およびサメ抽出脂質)の摂取がマウスL M 8 Dunn 骨肉種移植腫瘍の成長に及ぼす効果
-
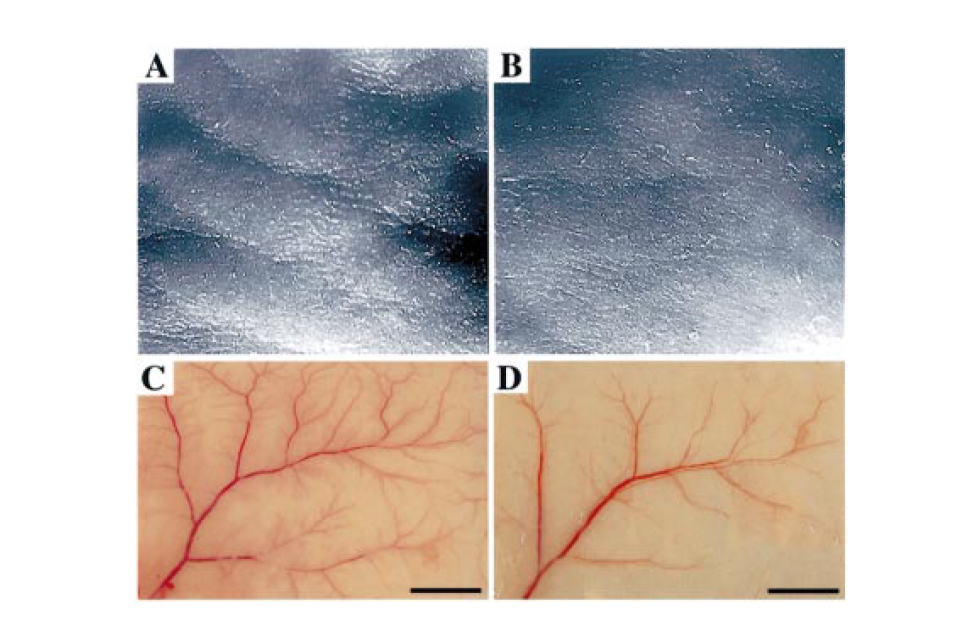 紫外線照射によるシワの発生と血管新生の形成Targeted Overexpression of the Angiogenesis Inhibitor Thrombospondin-1 in the Epidermis of Transgenic Mice Prevents Ultraviolet-B-Induced Angiogenesis and Cutaneous Photo-Damage
紫外線照射によるシワの発生と血管新生の形成Targeted Overexpression of the Angiogenesis Inhibitor Thrombospondin-1 in the Epidermis of Transgenic Mice Prevents Ultraviolet-B-Induced Angiogenesis and Cutaneous Photo-Damage


