The secret of keeping your youth “BONE”
We tend to think that bone is a hard mass of calcium. But when you take a good look inside of bone, there are so many various of cells wriggling. It has become known that those various cells contribute to bring youth to our body.
When the message substance from bone reaches the brain, it enhances memory. Furthermore, it increases the immunity of the body and protects us from diseases. On the contrary, when the message from bone were cut off, aging would accelerate as if the life switch had been turned off, degrading the immune system, memory and muscle strength. As long as bones are healthy, youth of the organs in the body are kept. Bone is the gatekeeper of youth.
There are about 200 bones in our body. The human body is a network. It became known that bones are one of the most important parts of the body-network, delivering a message that helps keep youth to our organs of the body.
The decline of BMD doesn’t simply mean that you got stuck. There is shocking data that one of 4 to 5 elderly people with femur fractures may die within one year (The 1-Year Mortality of patients Treated in Hip Fracture Program ). When BMD decreases, the youth-producing message from bones also drops, leading an aging process rapidly.
Bone is not only a stick supporting the body. but functions as an endocrine organ itself, producing special substances that bring youth to the human body. Therefore, weakened bones may reduce message substances, proceeding various aging symptoms.
What kind of messages does bone deliver?
1. Memory
If you struggle to remember new things lately, message substances from bones may be missing. US. Colombia University Professor, Dr. Gérard Karsenty found a message substance that delivered from bone to the brain. This is called “Osteocalcin”. (osteocalcin is a small size particle, less than 1/100000 mm). This substance has an important role in our memory. If the osteocalcin expressed from bone stopped, the function of hippocampus will slow down.
Osteocalcin expressed from bone is, so to speak, a command message to improve memory. This message is delivered into hippocampus through the blood vessels. The nerve cells in the hippocampus have special equipment to receive osteocalcin. When it receives osteocalcin, the brain starts working harder to improve memory.
“I was very impressed to find that bone also has a role to improve memory. As you know, our organs communicate to each other through message substances (communication factors). That means if the contents of this message were understood, the role of bone would be revealed furthermore”.
2. Increasing immune strength
For Japanese people, the main cause of death such as pneumonia and cancer, attribute to weakened immune system. Dr.Hermit Geiger (Professor, University of Ulm, Germany) who studies the mechanisms of aging, found that the message substances called Osteopontin decreases in aged mice.
“First, we divided aged mice into two groups, and one of them were given osteopontin. After five months, we observed a big change in the group being given osteopontin. We found that the number of immune cells that fights viruses in the body, was more than double compared with the mice not being given osteopontin”.
The message from osteopontin is, so to speak, increases the immune system. When these message substances reach the pre-immune cells, the amount of new- born immune cells go up, leading to increase the whole-body immunity.
Although it had been believed that bones were simply supporting the body, a recent study revealed that the dynamic role of bone, such as regulating the youth throughout the whole body by delivering messages.
3. Increasing muscle strength
Message substance, “osteocalcin” plays a role of enhancing the efficacy of muscular strength.
4. Enhance fertility
Osteocalcin plays another role such as increasing testosterone. Recent study showed that osteocalcin deficiency leads to decrease sperm cells.
Bone is a critical organ regulating our youth.
In order to retain our youth, what should we do? How to manage our bone strength? It is important to take enough calcium; however, recent study shows that only taking calcium is not good enough. It became known that bones themselves decide their strength by producing message substances.
Sclerostin expressed by bone delivers a message, “Stop making bones”, and it regulates bone mass growth in the body. “If we could control the amount of sclerostin in the body, we may keep our bone healthy and stay young”. Such expectations are rising.
At a glance, bone look still, but bones are constantly repeating bone metabolism that breaks old bones to create new bones. It is said that whole bones are completely reborn in about two to three years.
Sclerostin plays a role of brake. There is a factor that plays a role as an accelerator. By the balance of those message factors, bone mass in the body is decided. Bone is broken down by osteoclast, and is formed by osteoblast. Bones are constantly repeating bone metabolism that will prevent a stress fracture.
Where does the message substance come from?
Inside the pillars of the calcium (which means bone), other cells are hiding. These cells are called “bone cells.” Bone cells play a critical role expressing both brake and accelerator messages. Bone cell is, so to speak, a construction foreman.
In general, the size of a bone cell is 0.02 mm, the number of bone cells in the whole body is more than ten billion. As a result of adjusting those messages from bone cells, the construction of bones is determined.
Four messages that bring youth; (enhance memory, boost immune system, increase muscle strength, enhance fertility) Osteoblast is the cell producing those four messages. Osteoblast expresses the message substances called osteocalcin, and osteocalcin is delivered to the organs throughout the whole body via the blood vessels.
Among the elderly, bone fracture sometimes triggers aging symptoms such as dementia. Lately the importance of bone is in the spotlight.
-
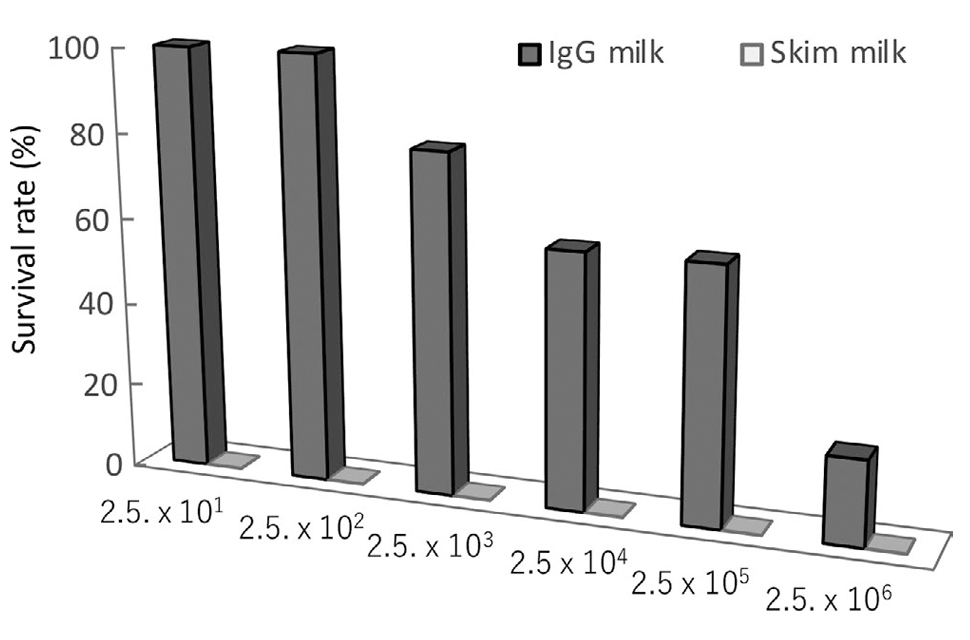 Enriched bovine IgG fraction prevents infections with Enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7, Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis, and Mycobacterium avium
Enriched bovine IgG fraction prevents infections with Enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli O157:H7, Salmonella enterica serovar Enteritidis, and Mycobacterium avium
-
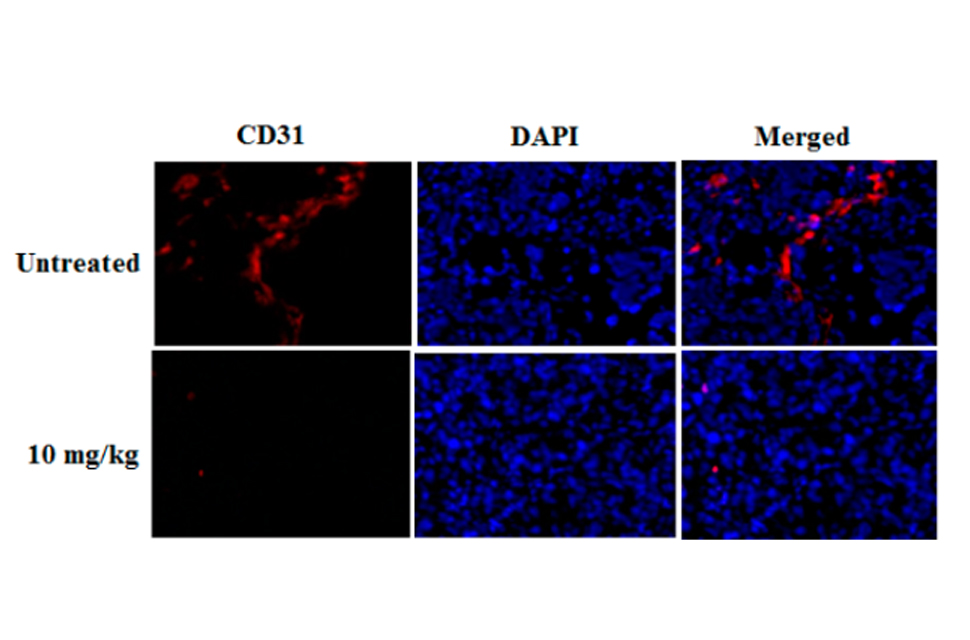 New Natural Pigment Fraction Isolated from Saw Palmetto: Potential for Adjuvant Therapy of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
New Natural Pigment Fraction Isolated from Saw Palmetto: Potential for Adjuvant Therapy of Hepatocellular Carcinoma
-
 Red pigment from Saw palmetto: A natural product for potential alternative cancer treatment
Red pigment from Saw palmetto: A natural product for potential alternative cancer treatment
-
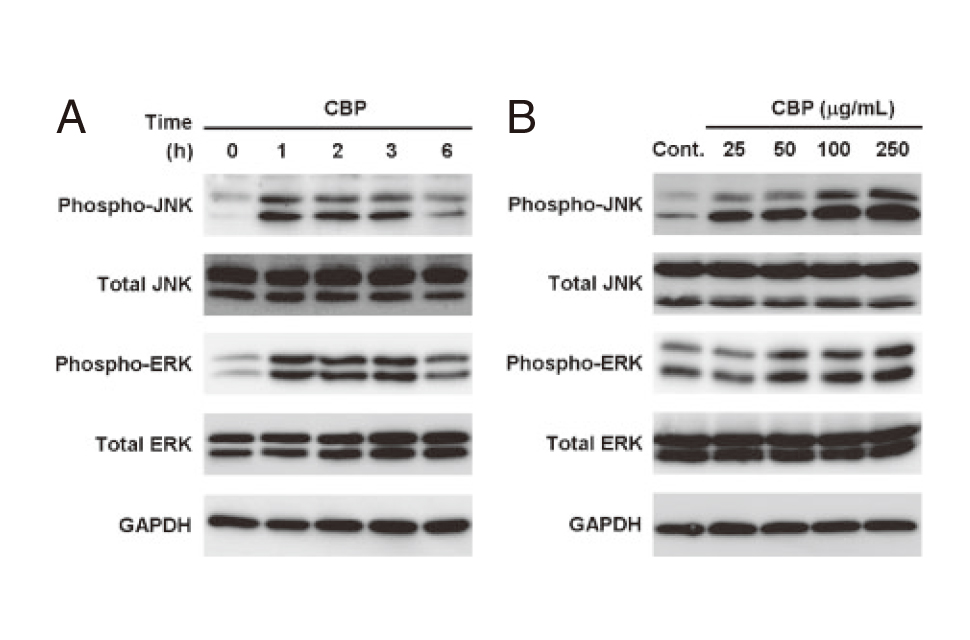 CBP Facilitate Osteogenesis through Activation of the JNK-ATF4 Pathway
CBP Facilitate Osteogenesis through Activation of the JNK-ATF4 Pathway
-
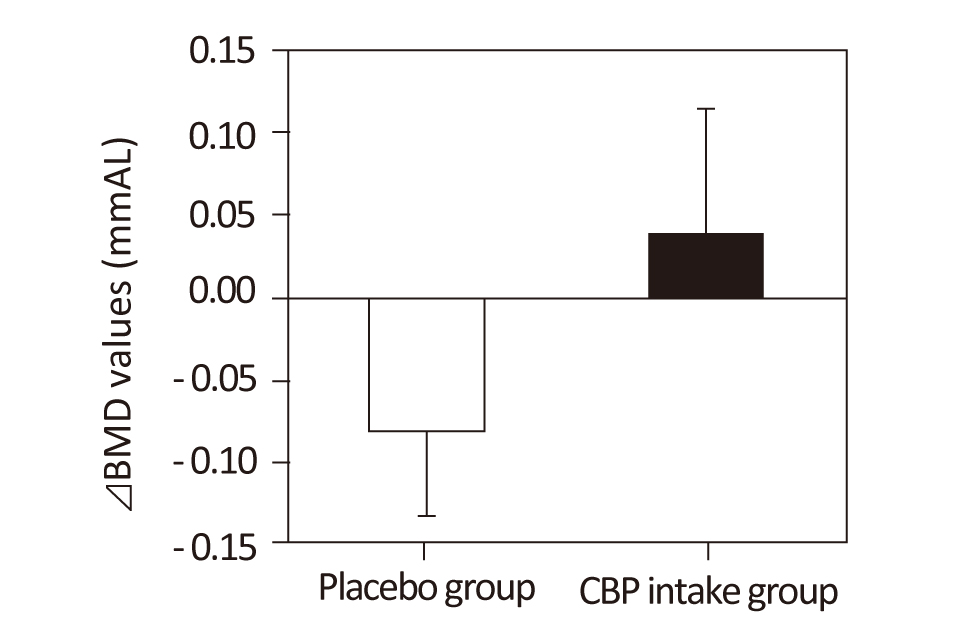 Concentrated-Bovine protein (CBP) increases Bone Mineral Density
Concentrated-Bovine protein (CBP) increases Bone Mineral Density
-
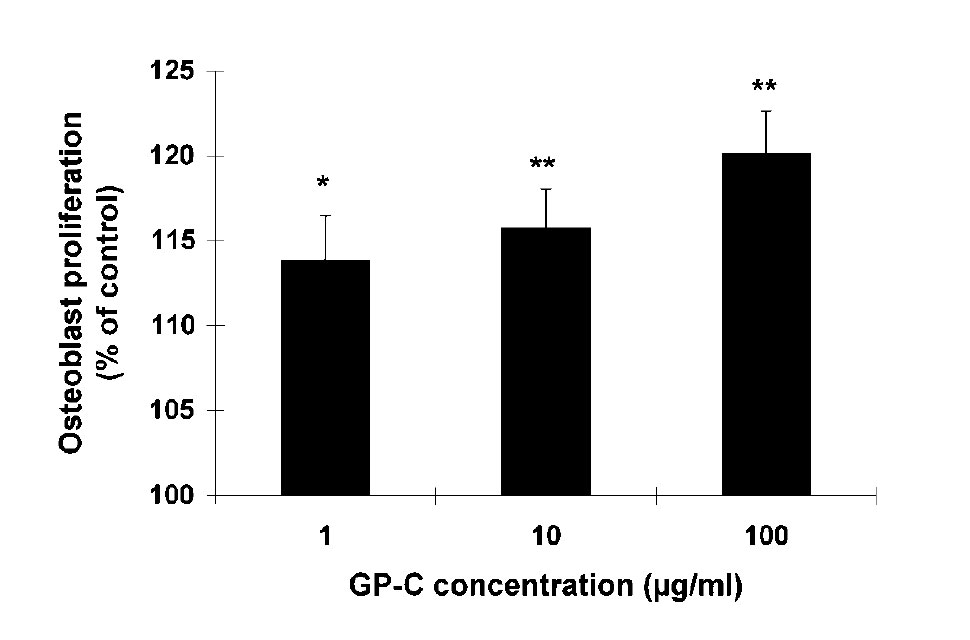 Effect of a Growth Protein-Colostrum Fraction on Bone Development in Juvenile Rats
Effect of a Growth Protein-Colostrum Fraction on Bone Development in Juvenile Rats
-
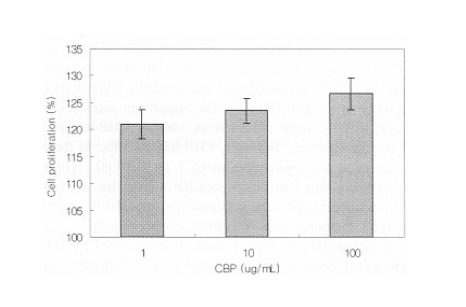 Effects of Colostrum Basic Protein from Colostrum Whey Protein: Increased in Osteoblast Proliferation and Bone Metabolism
Effects of Colostrum Basic Protein from Colostrum Whey Protein: Increased in Osteoblast Proliferation and Bone Metabolism
-
 An Ethanolic extract from a shark having potent anti-angiogenic activity: its anti-angiogenic mechanism and clinical application
An Ethanolic extract from a shark having potent anti-angiogenic activity: its anti-angiogenic mechanism and clinical application
-
 Shark Lipids for Treatment of Malignant Diseases
Shark Lipids for Treatment of Malignant Diseases
-
 Inhibition of Cancer Growth and Metastases by Preparations Based on Shark Oil
Inhibition of Cancer Growth and Metastases by Preparations Based on Shark Oil
-
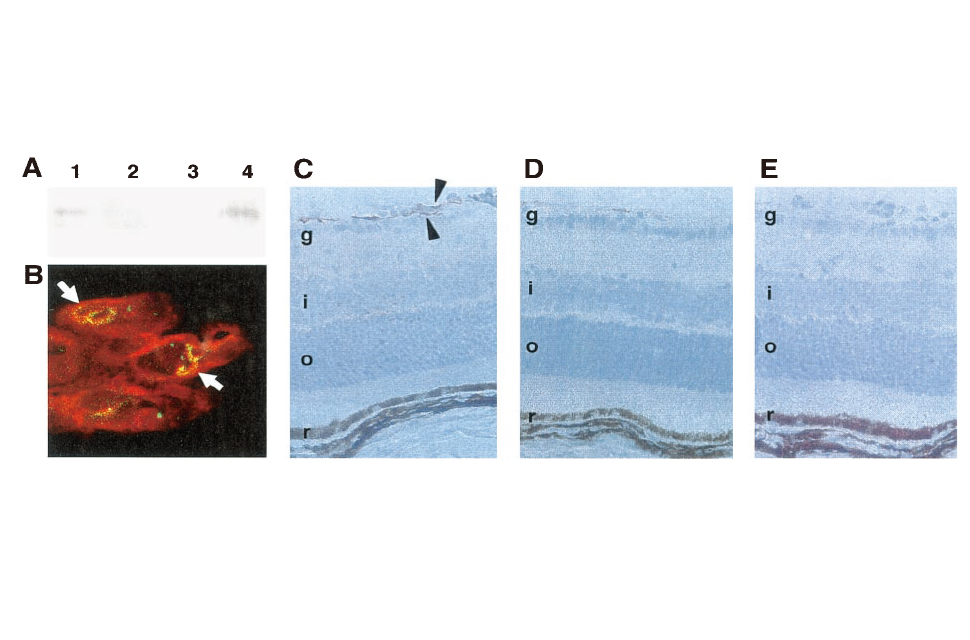 Leptin Stimulates Ischemia-Induced Retinal Neovascularization
Leptin Stimulates Ischemia-Induced Retinal Neovascularization
-
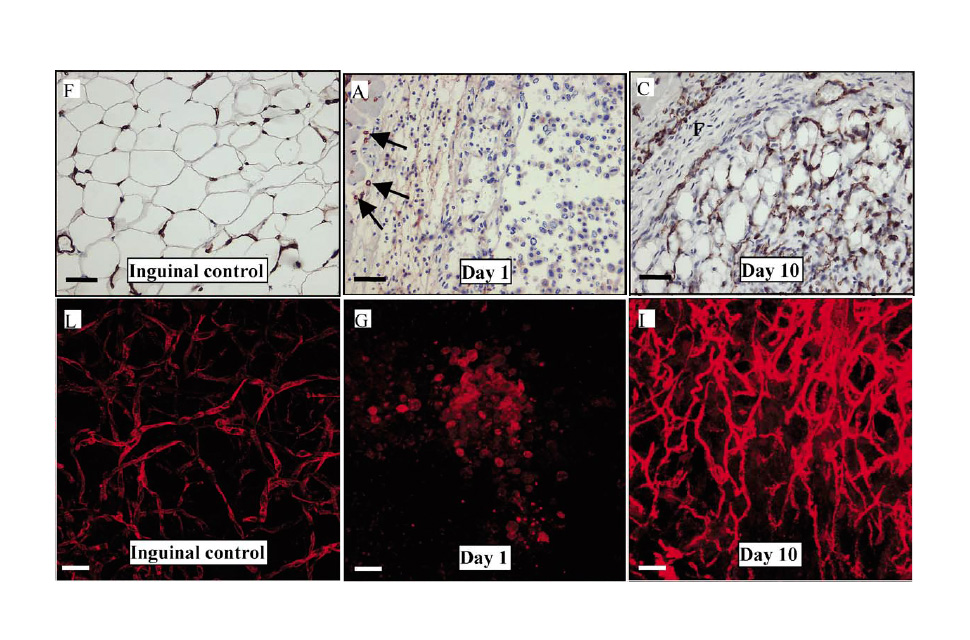 Angiogenesis in an in vivo model of adipose tissue development
Angiogenesis in an in vivo model of adipose tissue development
-
 The effects of functional foods, such as Agaricus, Pleurotus cornucopiae (Paulet) Rolland var. citrinopileatus (Sing.) Ohira. , Hericium erinaceum, Arabinoxylan, Shark cartilage and Shark extracted lipid on growth of implanted Mouse LM8 Dunn osteosarcoma
The effects of functional foods, such as Agaricus, Pleurotus cornucopiae (Paulet) Rolland var. citrinopileatus (Sing.) Ohira. , Hericium erinaceum, Arabinoxylan, Shark cartilage and Shark extracted lipid on growth of implanted Mouse LM8 Dunn osteosarcoma
-
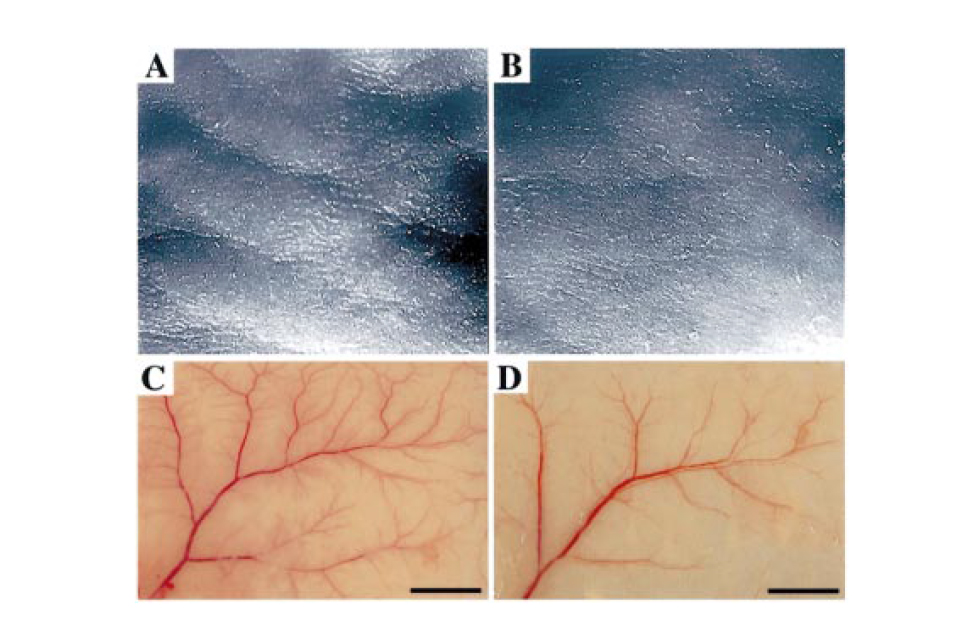 Targeted Overexpression of the Angiogenesis Inhibitor Thrombospondin-1 in the Epidermis of Transgenic Mice Prevents Ultraviolet-B-Induced Angiogenesis and Cutaneous Photo-Damage
Targeted Overexpression of the Angiogenesis Inhibitor Thrombospondin-1 in the Epidermis of Transgenic Mice Prevents Ultraviolet-B-Induced Angiogenesis and Cutaneous Photo-Damage


